Uniform Acceleration Formula
Acceleration. Observe the animation of the three cars below. Use the animation to answer the three questions. (If necessary, review the definition of acceleration.). 1.
Uniform Acceleration. Uniform acceleration occurs when the speed of an object changes at a constant rate. The acceleration is the same over time.
Physics is a mathematical science. The underlying concepts and principles have a mathematical basis. Throughout the course of our study of physics, we will encounter a variety of concepts that have a mathematical basis associated with them.
O n the scale of hurricanes and large mid-latitude storms, the Coriolis force causes the air to rotate around a low-pressure center in a cyclonic direction. Indeed, the term cyclonic not only means that the fluid (air or water) rotates in the same direction as the underlying Earth, but also that the rotation of the fluid is due to the rotation
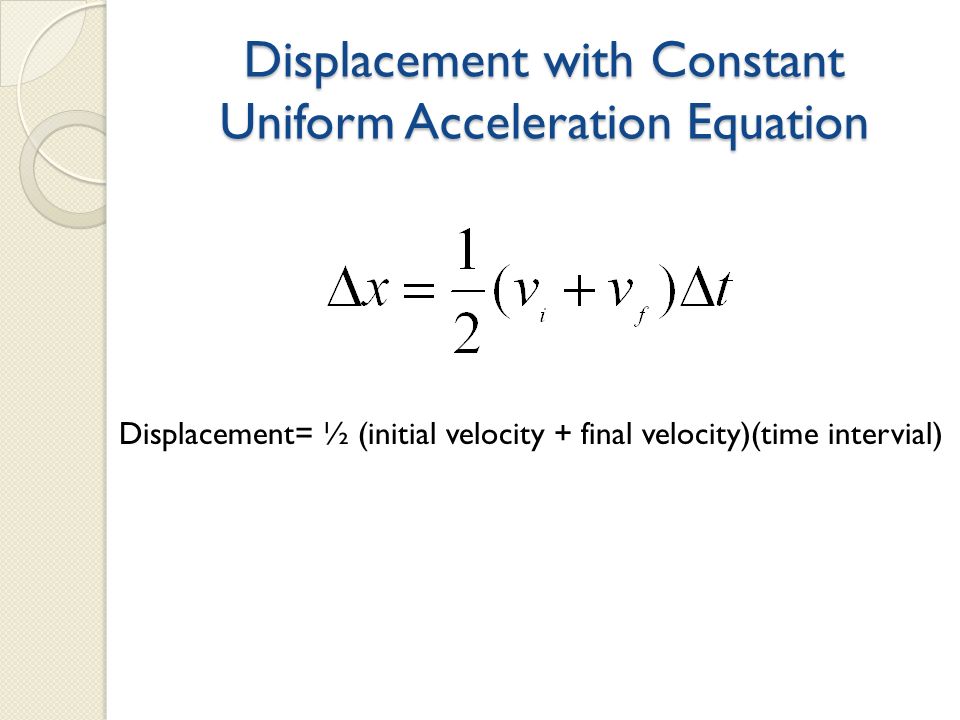
Gerry Murphy. 11/7/2002 2. Derivation of the Airborne Speed Formula. z. This Derivation results in an equation that can be used for . ALL. airborne applications
UNChem Glossary. Click on the first letter of the term. [][][][][][f][][][][j][][][][][][][][][][][u][][][x][y][z]UNChem Main Page or Shodor Home Page. A acceleration Measure of how fast velocity is changing, so we can think of it as the change in velocity over change in time.
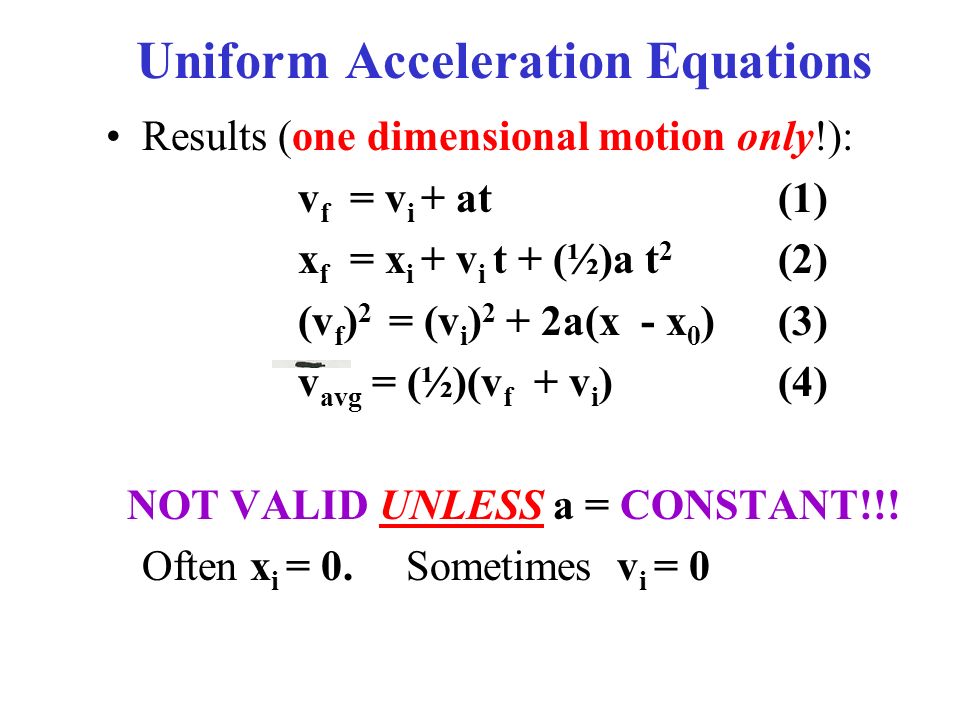
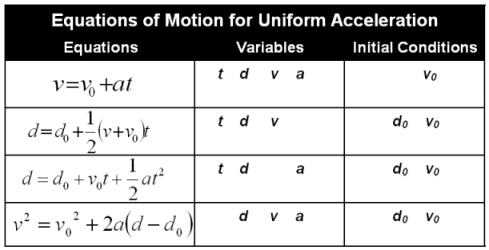
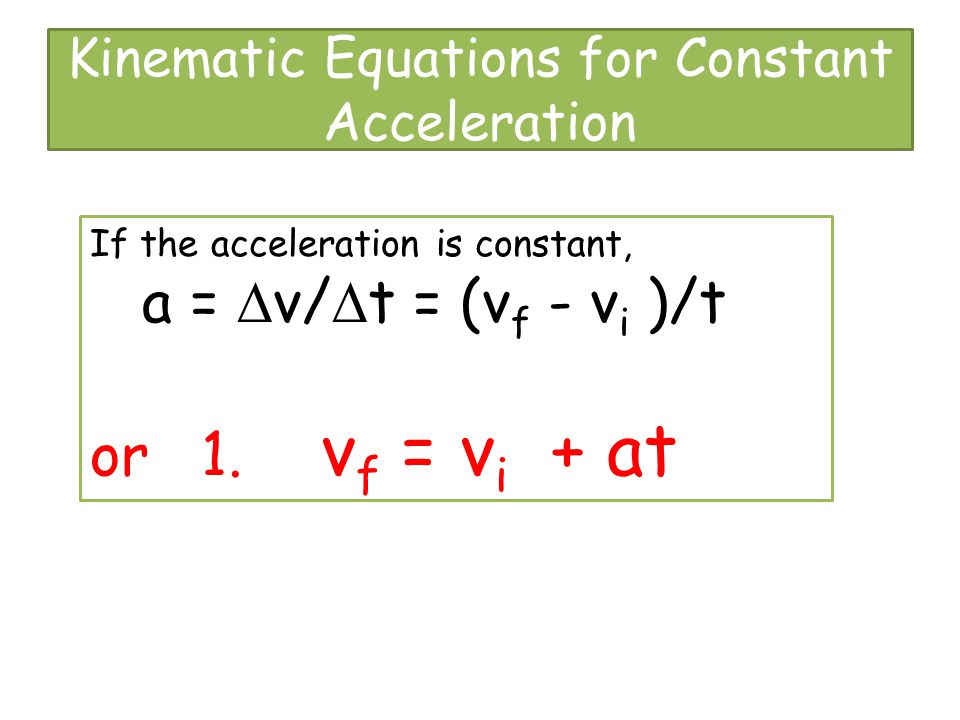
This episode continues to look at basic kinematics and introduces the equations of motion for uniform acceleration. This involves a little calculation practice.
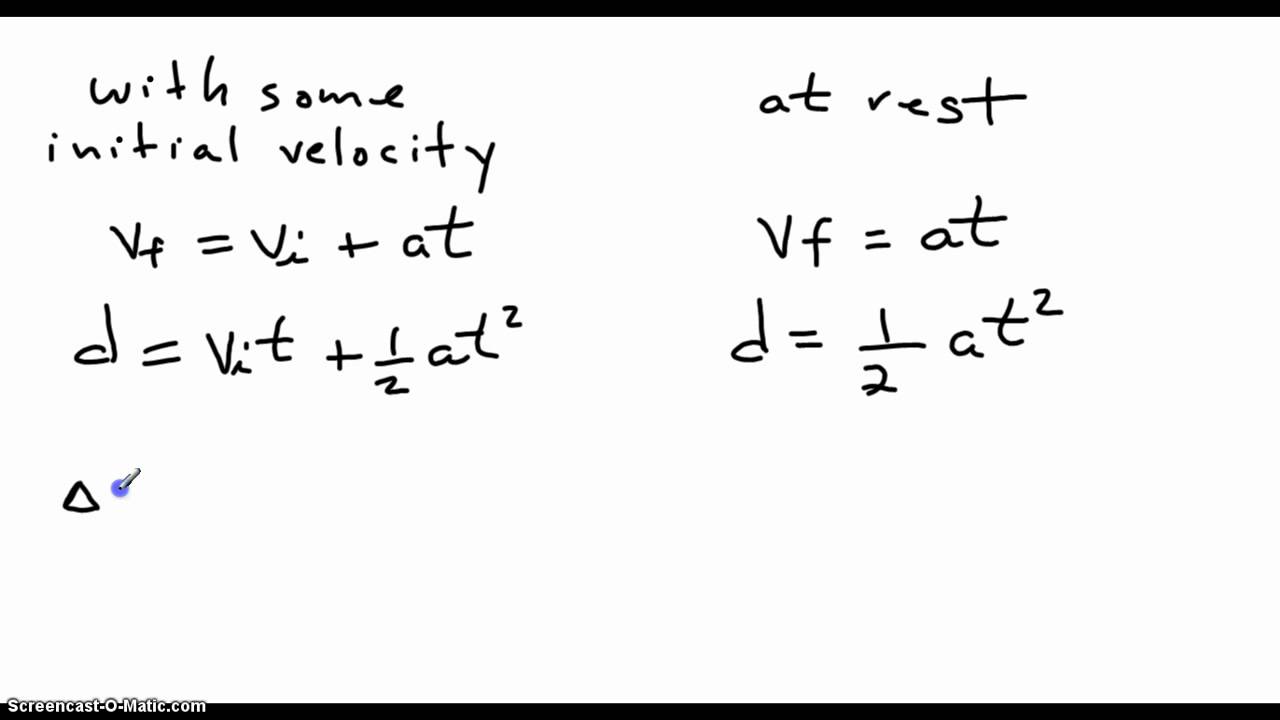



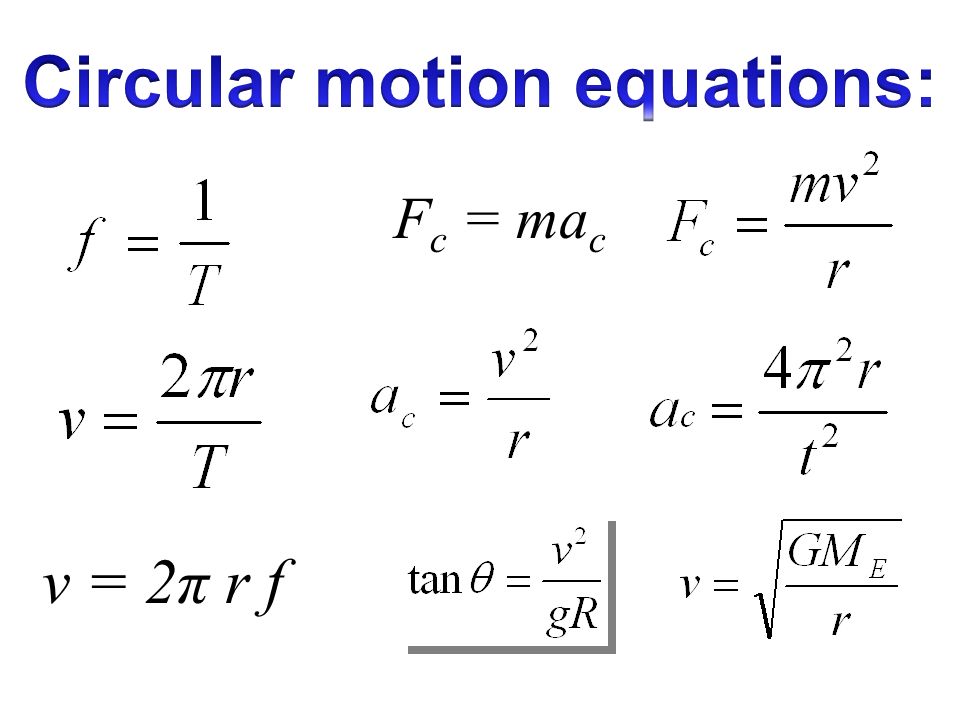
In physics, circular motion is a movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular path. It can be uniform, with constant angular rate of rotation and constant speed, or non-uniform with a changing rate of rotation.
Acceleration of an object is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. SI unit is metre per second square or metre per second per second ($m \, s^{-2}$) Vector quantity $ a = \frac{v – u}{t}$, where v is final velocity, u is initial velocity and t is time taken.
From the instantaneous position r = r(t), instantaneous meaning at an instant value of time t, the instantaneous velocity v = v(t) and acceleration a = a(t) have the general, coordinate-independent definitions;
